This Drawing Shows the Plan of Arc

Plans are a set of drawings or two-dimensional diagrams used to describe a place or object, or to communicate building or fabrication instructions. Ordinarily plans are drawn or printed on paper, simply they tin take the grade of a digital file.
Plans are used in a range of fields: compages, urban planning, landscape architecture, mechanical engineering, civil engineering, industrial engineering to systems engineering.
The term "plan" may casually be used to refer to a single view, sheet, or drawing in a set of plans. More specifically a plan view is an orthographic projection looking downward on the object, such every bit in a flooring plan.
Overview [edit]
Plans are frequently for technical purposes such every bit architecture, technology, or planning. Their purpose in these disciplines is to accurately and unambiguously capture all the geometric features of a site, building, product or component. Plans can likewise be for presentation or orientation purposes, and are often less detailed versions of the erstwhile. The stop goal of plans is either to portray an existing place or object, or to convey enough data to allow a builder or manufacturer to realize a design.
The procedure of producing plans, and the skill of producing them, is often referred to as technical drawing. A working cartoon is a type of technical drawing, which is function of the documentation needed to build an technology product or architecture. Typically in architecture these could include ceremonious drawings, architectural drawings, structural drawings, mechanical drawings, electrical drawings, and plumbing drawings. In technology, these drawings show all necessary information to manufacture a given object, such as dimensions and angles.
Plan features [edit]
Format [edit]
Plans are often prepared in a "set". The set includes all the information required for the purpose of the set, and may exclude views or projections which are unnecessary. A set of plans can be on standard function-sized paper or on large sheets. It can exist stapled, folded or rolled as required. A set of plans tin likewise have the form of a digital file in a proprietary format such as DWG or an commutation file format such as DXF or PDF.
Plans are often referred to as "blueprints" or "bluelines". However, the terms are rapidly condign an anachronism, since these copying methods have more often than not been superseded by reproduction processes that yield black or multicolour lines on white paper, or by electronic representations of information.
Calibration [edit]
Plans are unremarkably "scale drawings", pregnant that the plans are drawn at a specific ratio relative to the actual size of the place or object. Various scales may exist used for different drawings in a set. For example, a flooring programme may be drawn at ane:48 (or 1/4"=1'-0") whereas a detailed view may exist fatigued at i:24 (or 1/2"=i'-0"). Site plans are ofttimes fatigued at 1" = 20' (one:240) or 1" = xxx' (1:360).
In the metric arrangement the ratios commonly are ane:five, 1:10, 1:20, 1:50, ane:100, i:200, i:500, 1:1000, one:2000 and i:5000
Views and projections [edit]

Symbols used to define whether a project is either 3rd Angle (right) or Start Angle (left).

Because plans stand for three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional aeroplane, the use of views or projections is crucial to the legibility of plans. Each projection is achieved past assuming a vantage point from which to see the place or object, and a type of projection. These project types are:
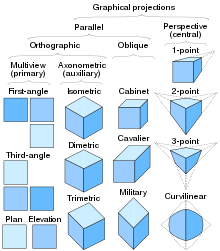
Classification of Plan (drawing) and some 3D projections
- Parallel projection
- Orthographic projection
- Multiview project, including:
- Plan view or floor plan view
- Elevation, ordinarily a side view of an exterior
- Section, a view of the interior at a particular cutting plane
- Axonometric project, including:
- Isometric project
- Dimetric projection
- Trimetric projection
- Multiview project, including:
- Oblique project, and
- Orthographic projection
- Perspective projection, including:
- One-signal perspective
- Two-bespeak perspective
- Three-bespeak perspective
Planning approach [edit]
There is no universal standard for sheet order, still the post-obit describes a common approach:
- Full general Data : The first sheets in a fix may include notes, assembly descriptions, a rendering of the projection, or simply the projection title.
- Site : Site plans, including a key plan, appear earlier other plans and on smaller projects may be on the first canvas. A project could require a mural plan, although this can be integrated with the site plan if the drawing remains clear.
- Specific plans : Floor plans, starting with the lowest floor and ending with the roof program unremarkably appear near the beginning of the set. Further, for example, reflected Ceiling Plans (RCP)due south showing ceiling layouts appear after the floor plans.
- Elevations : Starting with the master, or front meridian, all the building elevations appear later the plans. Smaller residential projects may display the elevations before the plans. Tiptop details may appear on the aforementioned sheets as the edifice elevations.
- Sections: Building sections that draw views cutting through the unabridged building announced side by side, followed by wall sections, then item sections.
- Details: Details may appear on any of the previous sheets, or may exist collected to appear on detail sheets. These details may include construction details that bear witness how the components of the building fit together. These details may as well include millwork drawings or other interior details.
- Schedules: Many aspects of a edifice must be listed as schedules on larger projects. These include schedules for windows, doors, wall or flooring finishes, hardware, landscaping elements, rooms, and areas.
Where boosted systems are complex and require many details for installation, specialized boosted plan drawings may be used, such as:
- Structural: While smaller projects may merely show structural information on the plans and sections, larger projects take split up sheets describing the structure of the building.
- Mechanical: Mechanical drawings show plumbing, heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, or burn down protection systems.
- Electrical :Electrical program drawings may include equipment and cable tray layout, lighting and ability, grounding, phone, local area network, special communications or signal systems, or a reflected lighting programme.
See also [edit]
- Architectural drawing
- Blueprint
- Engineering cartoon
- Floor plan
- Firm plan
- Plat
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plan_%28drawing%29
0 Response to "This Drawing Shows the Plan of Arc"
Post a Comment